It’s natural to wonder when snake season begins – and if you’re living in an area with snakes, it’s important to know when to be extra vigilant. To help you understand when snake season starts and ends, we’ve put together this comprehensive guide to everything you need to know about snake season.
Types of Snakes

1. Venomous Snakes
Venomous snakes have evolved their venom to help them capture prey, while also providing protection against predators. Some of the most common venomous snakes include rattlesnakes, cobras, mambas, and vipers.
2. Non-Venomous Snakes
Non-venomous snakes use constriction to capture prey and have evolved to live in a wide variety of habitats. Some of the most common non-venomous snakes include pythons, boas, and garter snakes.
Climate and Temperature
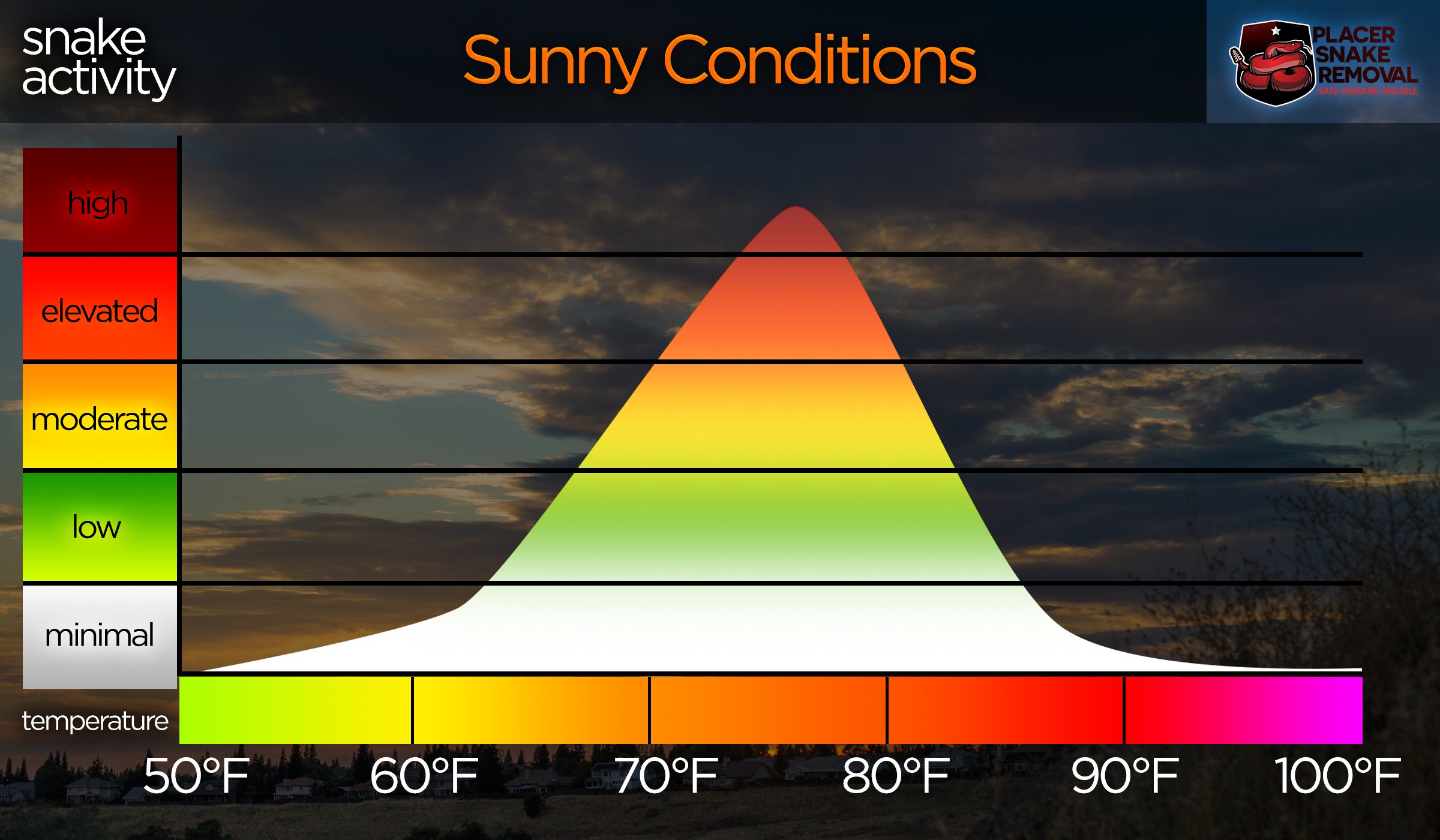
- Snakes are cold-blooded, meaning they rely on their environment to regulate their body temperature.
- During the hot summer months, snakes become more active as the warm temperatures provide them with the energy they need to hunt.
- In the winter, snakes become less active as the cold temperatures slow down their metabolism.
- The climate of an area can also affect when snakes are most active. In areas with milder climates, snakes may be active year-round, while in areas with more extreme climates, snakes may be most active during certain times of the year.
When Do Snakes Come Out In Georgia?

- In Georgia, most snakes emerge from hibernation in the spring, typically March or April.
- They may come out earlier if the weather is unseasonably warm.
- In the summer months, snakes are active during the night and can often be seen during the day.
- In the fall, snakes become less active and enter hibernation in October or November.
When Are Snakes Most Active In Georgia?

| Season | Activity Level |
|---|---|
| Spring | Most snakes are active in the spring, with some species beginning their activity as early as February. |
| Summer | Snakes become more active in the summer months, as the temperatures increase. This is the time when they are most likely to be seen in the open. |
| Fall | As temperatures begin to cool, snakes become less active and start to seek shelter in dens. However, they can still be found out and about during this time. |
| Winter | During the cold winter months, snakes become dormant and are rarely seen. Some species may remain active in areas with mild temperatures. |
In Georgia, snakes are most active from spring through fall. As the temperatures rise in the spring, snakes become more active and are more likely to be seen in the open. During the summer months, their activity peaks, and they can be found in many places. As temperatures begin to cool in the fall, snakes become less active and will seek shelter in dens. In the winter, their activity slows significantly, and they become dormant in most areas.
Favorable Habitats for Snakes

Snakes are found in a variety of habitats. They can live in wetlands, deserts, forests, grasslands, and even in urban areas. The type of habitat a snake prefers depends on the species. Generally, snakes prefer habitats with a warm climate, plenty of hiding places, and access to food.
| Habitat | Climate | Hiding Places | Food |
| Wetlands | Warm | Trees, Rocks, Burrows | Fish, Frogs, other aquatic life |
| Deserts | Hot | Bushes, Shrubs, Rocks | Small mammals, Birds, Lizards |
| Forests | Mild | Logs, Rocks, Burrows | Small mammals, Birds, Reptiles |
| Grasslands | Mild | Logs, Rocks, Burrows | Small mammals, Birds, Reptiles |
| Urban Areas | Mild | Shrubbery, Rocks, Burrows | Insects, Rodents, Lizards |
Food Sources for Snakes

- Insects: Most snakes feed on insects such as grasshoppers, crickets, caterpillars, beetles, and moths.
- Small Mammals: Small mammals such as mice, rats, voles, and rabbits are often consumed by snakes.
- Amphibians: Amphibians such as frogs and salamanders are commonly eaten by snakes.
- Birds: Snakes are also known to eat small birds such as sparrows, quails and hummingbirds.
- Reptiles: Reptiles such as lizards, turtles, and other snakes are also potential prey items for some species of snakes.
- Fish: Some aquatic species of snakes feed on small fish.
- Eggs: Snakes also feed on eggs of other animals, including birds and reptiles.
Snake Activity During Breeding
During the breeding season, snakes become more active and can be seen in areas they usually avoid. They may also become more aggressive when defending their territory. Males will engage in courtship displays, such as body undulations and head bobbing, to attract females for mating. Females will lay eggs in a protected, warm environment, such as an underground burrow or the hollow of a tree. After the eggs hatch, the young snakes will typically stay close to their mother for a few days before dispersing into the wild.
Snake Migration Patterns
Snakes are cold-blooded animals, which means that they cannot regulate their own body temperature. As a result, they have to migrate to find warmer climates during the winter months. Many snakes hibernate during the cold winter months, and when the temperature starts to rise again in the spring, they will come out of hibernation and begin migrating to their summer habitats.
Migration routes can vary depending on the species and their particular needs, but there are some general patterns that are common among most species. Some snakes may migrate several hundred miles to find a suitable summer habitat, while others may only migrate a few miles. Generally, snakes will migrate to areas with abundant food sources, shelter, and warmth.
| Species | Migration Route |
|---|---|
| Garter Snake | Migrate short distances to find food and shelter. |
| Pine Snake | Migrate long distances to find warmer climates. |
| Rattlesnake | Migrate moderate distances to find food, shelter, and warmth. |
In some cases, snakes may migrate in large groups or even form migratory clusters. As the temperatures cool down in the fall, snakes will begin migrating back to their winter habitats. Of course, some snakes will not migrate; they will remain in their summer habitats year-round. The best time for you to observe snake migration patterns is in the spring and fall when snakes are most active.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Snake Season in Georgia?
Snake season in Georgia typically runs from March to October, with the most active period being between April and October. Many species of snake are active during these months, including rat snakes, copperheads, cottonmouths, and rattlesnakes. It is important to be aware of where snakes may be present during these months and take appropriate precautions.
When are Snakes Most Active in the Region?
Snakes are most active in the region during the warmer months of the year when temperatures are higher and food sources are abundant. These months typically include May through August, when daytime temperatures are at their highest. However, depending on the species of snake, they may be active during the cooler months as well.
What Time of Year Do Snakes Come Out in Georgia?
In Georgia, snakes are generally active from late March to early October, when temperatures are warm enough for them to emerge from hibernation. During this period, they can be seen basking in the sun or searching for food. During the colder months of November to February, snakes will go dormant and hide in burrows, logs, or other warm places to keep warm.
How can I protect myself during snake season in Georgia?
Wear long pants and boots when walking in areas where snakes are likely to be present. Be mindful when reaching into areas that cannot be easily seen, such as beneath rocks or logs. Be aware of your surroundings and watch for snakes, particularly when walking through tall grass or near rocks or logs. If a snake is spotted, give it a wide berth and do not attempt to disturb or handle it. If hiking, carry a walking stick and use it to check areas ahead of you where snakes might be hiding. Consider snake-proofing your property by clearing away debris, creating barriers such as fences, and using snake repellents.
What can I do to keep snakes away during their active season?
Snakes can be deterred from entering your property by eliminating potential hiding places and food sources, such as tall grass, brush piles, and bird feeders. If possible, close off gaps and cracks in your home’s foundation. Inspect items that have been stored outside for a long period of time before bringing them inside. Trim trees and shrubs away from your home and remove clutter from the yard. Finally, install a tight-fitting door sweep on all exterior doors.
Conclusion
Snakes are an important part of our ecosystem, and understanding when snake season is can help us coexist with them. Snake season typically runs from spring to fall, but can vary in different climates and regions. The best way to protect yourself and others is to be aware of your surroundings, learn how to identify venomous snakes, and know what to do if you come across one.
- Klauber, Laurence M. “Rattlesnakes: Their Habits, Life Histories, and Influence On Mankind”. University of California Press, 1972. https://www.ucpress.edu/book/9780520022917/rattlesnakes
- Tucker, J. Kevin and Joseph R. Mendelson III. “Snakes of the Southeast”. University of Georgia Press, 2010. https://www.ugapress.org/book/9780820330521/snakes-of-the-southeast/






